By: Dr Pankaj Ranjan
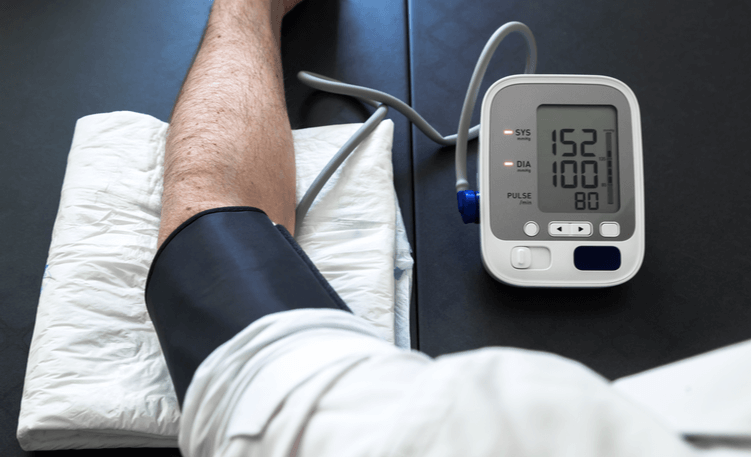
Cardiac ailments have swiftly risen to prominence as the leading cause of mortality in India and globally, claiming the lives of approximately 1 in 5 men and 1 in 8 women, according to reports from the World Health Organization (WHO). This surge is primarily attributed to the accumulation of fatty substances in the arteries, causing a blockade in the heart’s blood supply—a condition exacerbated by lifestyle factors such as smoking, obesity, high cholesterol, elevated blood pressure, and diabetes.
In a noteworthy departure from the conventional association of heart attacks with old age, an alarming trend has surfaced, with an increasing number of individuals in their 20s, 30s, and 40s grappling with heart-related ailments. The escalating stress levels inherent in modern life have exposed even the younger demographic to the perils of heart diseases. While genetic predisposition and family history remain uncontrollable risk factors, the majority of heart diseases among the youth are linked to excessive stress, prolonged working hours, erratic sleep patterns, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle, all of which contribute to inflammation and escalate the risk of heart-related issues.
Startling statistics reveal that every day witnesses approximately 9,000 fatalities due to heart ailments, translating to one life lost every 10 seconds. Alarmingly, 900 of these casualties belong to the youth demographic, those below 40 years of age. Urgent and widespread education is crucial to stave off the impending epidemic of heart diseases in India, lest it becomes the leading cause of mortality by 2020.
While cardiac hospitals in India perform over 200,000 open-heart surgeries annually, witnessing a 25% annual increase, these interventions are merely palliative measures. The key to mitigating the prevalence of heart attacks lies in comprehensive public education about heart diseases and their risk factors.
Recognizing the Symptoms:
Symptoms of coronary heart disease (CHD) can vary widely, with angina chest pain being a common feature. Ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain, individuals may experience sensations akin to indigestion or intense pain, heaviness, or tightness. Pain typically centers in the chest and may radiate to the arms, neck, jaw, or stomach, accompanied by palpitations and abnormal breathlessness.
Prognosis and Diagnostic Measures:
Early assessment of a suspected CHD patient involves a comprehensive examination of medical and family history, lifestyle evaluation, and blood tests. Confirmatory diagnostic tests include non-invasive procedures such as electrocardiogram (ECG), X-ray, treadmill test (TMT), cardiovascular cartography, CT angiography, and invasive coronary angiography.
Management of Heart Ailments:
Although coronary heart disease cannot be cured, effective management involves a multifaceted approach encompassing lifestyle changes, medications, and non-invasive treatments. Severe cases may necessitate invasive and surgical interventions. Lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, abstinence from smoking, and control of blood cholesterol and sugar levels, significantly reduce the risk of CHD, stroke, and dementia.
Treatment Options:
Various medications are employed to treat CHD, targeting cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes. While these medications are generally effective, periodic blood tests are recommended due to potential side effects. Advancements in medical science have led to less invasive surgical methods, such as Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG), valve replacement surgeries, Minimally Invasive Direct Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (MIDCAB), Thoracic surgeries with VATS, and management of heart and lung failure using Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO).
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) plays a crucial role in managing progressive heart failure by synchronizing the contractions of the heart’s chambers. This innovative treatment involves implanting a device that coordinates the heart’s rhythm, enhancing its efficiency and alleviating symptoms. CRT significantly improves the quality of life for individuals facing advanced heart failure.
Demystifying Heart Failure:
Contrary to its ominous name, heart failure can be managed effectively with improved care and diagnosis. Prevention revolves around avoiding lifestyle and dietary habits that contribute to obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure. A healthy lifestyle remains the simplest and most effective means of warding off heart failure and ensuring optimal heart function. (The author is the HOD & Senior Consultant, Cardiac Sciences, Yatharth Super Specialty Hospital, Greater Noida)