The natural changes of the body with ageing can affect mobility, balance, and lifestyle. As the ageing population continues to grow, so does the rising demand for specialist methods of elder care. Physiotherapy is a central part of quality elder care, offering examples of tailored methods of supporting older adults in the right way to participate in independence and functional activities for as long as possible.
The Vital Role of Physiotherapy in Modern Elder Care
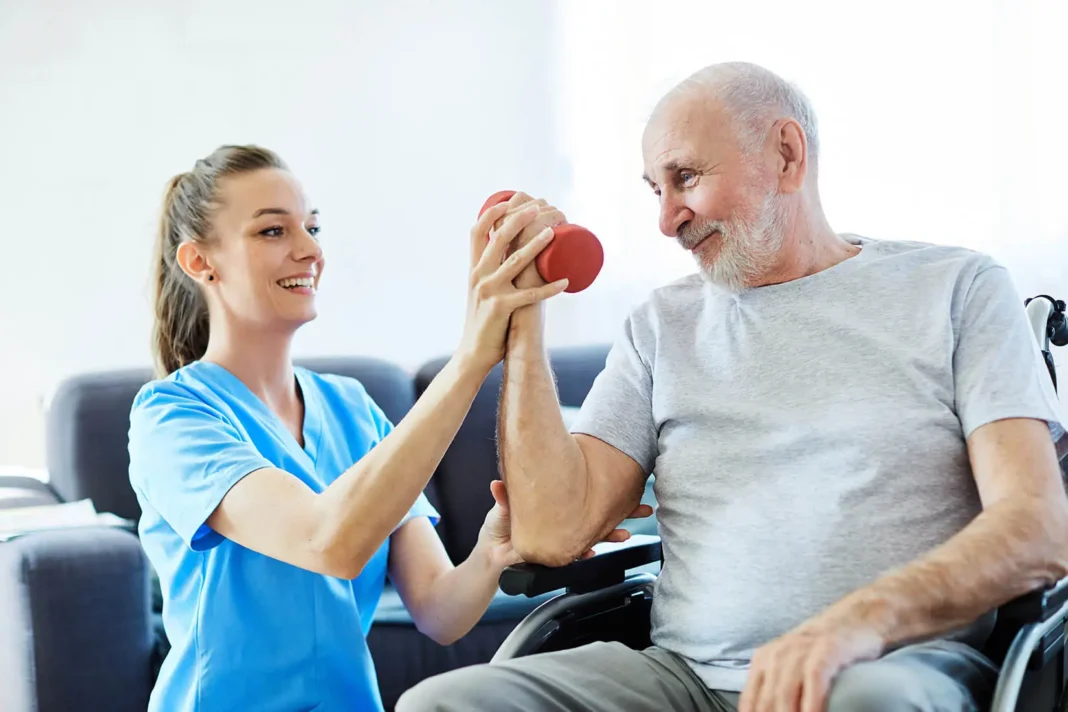
Physiotherapy for older people involves more than ordered exercises. Instead, it is a holistic approach to the management of older people with physical changes associated with age through evidence-based strategies. For most older people, physiotherapy is the bridge between medical treatment and going back to daily activities with confidence. Physiotherapy in care of older people has among its goals the preservation or improvement of mobility.
Physiotherapists offer specific exercises and movement strategies to the elderly in order to maintain their capacity to walk, transfer between positions, and navigate within their environment in a secure way. This functional movement emphasis is in direct relation with increased independence for the elderly to perform daily activities with greater confidence and minimal support.
Key Benefits of Physiotherapy for Older Adults
Improved Mobility and Independence
One of the major objectives of physiotherapy in geriatric care is to sustain or enhance mobility. By applying specific exercises and movement strategies, physiotherapists assist older adults in maintaining their walking ability, moving from one position to another, and safely mobilizing within their surroundings. Functional movement directly addresses prolonged independence as older adults are able to carry out daily functions with minimal support.
Preventing Falls and Balance Training
Falls can pose a serious hazard to the well being of older individuals, resulting in serious injury and a diminished sense of confidence in their mobility. Physiotherapy provides a solution with targeted balance retraining and strength exercises that emphasise specific muscles used for balance. The observation of gait and environmental modifications are all important aspects of comprehensive fall prevention programs.
Pain Management in Chronic Conditions
As stated before, a lot of older persons will certainly have chronic illnesses such as arthritis, osteoporosis, or chronic back pain that will interfere with conducting normal daily functions. Physiotherapy serves to manage pain without reliance on medication where therapeutics, exercises, and temperature applications (heat or cold) reduce the need for drugs and enable an older person to get on with daily life.
Post-Operative and Trauma Healing
Recovery from injury or surgery can also be very difficult for older adults. Physiotherapy will provide structured rehabilitation programs to make recovery easier and less risky. One can apply physiotherapy after hip replacement, stroke, or cardiovascular disorder, specific rehabilitation programs that will serve the purpose of helping the elderly recover function and strength and reduce complications.
Expert Physiotherapy Techniques in Elder Care
Contemporary physiotherapy in aged-care environments utilises a range of specialised techniques:
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on treatments that enhance joint mobility, alleviate pain, and increase tissue flexibility.
- Therapeutic Exercise Programs: Individualized routines of strength, endurance, flexibility, and balance, each tailored to a person’s ability.
- Aquatic Therapy: Exercising in water minimises joint stress and offers natural resistance, especially for arthritis or mobility restriction sufferers.
- Vestibular Rehabilitation: Tailor-made exercises that target inner ear conditions influencing balance and spatial orientation.
- Respiratory Physiotherapy: Breathing efficiency and airway clearance techniques are particularly relevant for individuals with respiratory disorders.
Implementing Effective Physiotherapy in Elder Care Settings
The integration of physiotherapy into comprehensive elder care requires thoughtful implementation:
Personalised Assessment and Goal Setting
Physiotherapy that works must always start with a robust assessment of physical functioning pertinent to the medical history and the personal goals of each older adult. This individualization guarantees that the treatment given has the best fit for the unique needs of the individual rather than a generalized approach.
Collaborative Care Approaches
Collaborative care Models Physiotherapy in long-term care facilities works as an interdisciplinary team with specialists, physicians, occupational therapists, nurses, and caregivers. This collaboration gives space for physiotherapy to support other health elements and allows all team members to work toward common goals.
Education and Empowerment
Education and Self-Efficacy In elder-focused physiotherapy, it is about more than only using direct intervention. It is about sharing important information regarding safe mobilisation strategies, exercises to do at home, and adaptations to their environment for older adults and their caregivers. This approach empowers older adults to be responsible for their own physical health.
Tracking Progress and Adapting Interventions
Physiotherapists keep on assessing the kinetic activity in order to determine the improvements and to change the physiotherapy aids according to that change. This constant repetition and flexibility in approach allows updated practice in light of the ever-changing set of circumstances that engage itself with the needs of the individual.
The Future of Physiotherapy in Elder Care
As we learn more and more about the ageing process, the role of elder care keeps on evolving. We are on the verge of experiencing exciting new technologies such as telehealth platforms which will allow seniors to go to physiotherapy from home. Also, wearable technology has come in place to give real-time feedback about movement and adherence to exercise routines.
Ongoing research is shedding light on how physiotherapy can truly enhance the lives of older adults. There’s a growing body of evidence that highlights the benefits of physiotherapy for cognitive health, fall prevention, and the management of more complex conditions like Parkinson’s disease and dementia.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy is a vital part of quality aged care that delivers evidence-based strategies to enhance mobility, alleviate pain, prevent falls, and enhance quality of life. By understanding and addressing the special physical limitations commonly associated with aging, physiotherapy helps older persons maintain their independence and dignity.
For those families caught up in elder care matters, integrating everyday physiotherapy service possibilities is capable of striking a difference for outcomes. No matter whether accessed through home health services, clinics, or retirements homes, effective access to physiotherapy can enhance ageing in place, as well as the elder care experience for those directly impacted families.